SCEMBLIX targets the abnormal protein that causes Ph+ CML in chronic phase differently
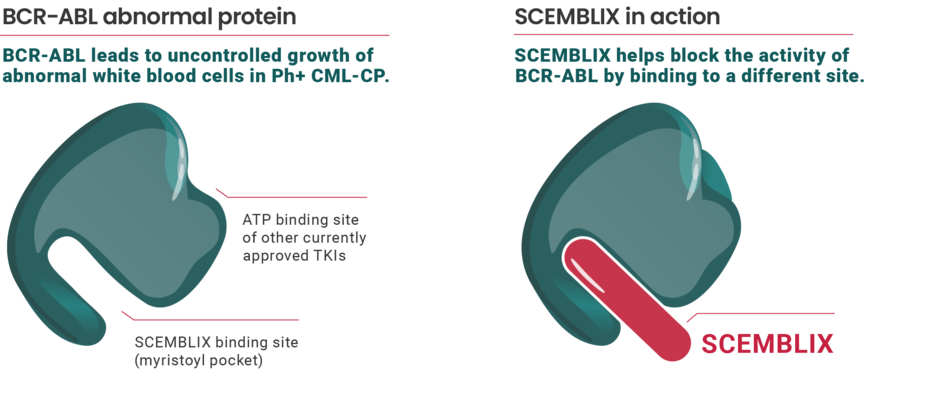
SCEMBLIX is thought to work by binding to a different site (myristoyl pocket) to help block the activity of the abnormal protein that causes Ph+ CML in chronic phase.
Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) is caused by a continuously active abnormal protein (BCR-ABL) that leads to uncontrolled growth of abnormal white blood cells (also known as leukemic cells).
All other currently approved tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) bind to this abnormal protein at a site known as the ATP binding site to help block the protein's activity.
SCEMBLIX targets a different site of this abnormal protein to help block the protein's activity.
ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Ph+ CML-CP, Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase; TKIs, tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
*SCEMBLIX was studied vs GLEEVEC® (imatinib), TASIGNA® (nilotinib), Sprycel ® (dasatinib), and Bosulif ® (bosutinib). Sprycel is a registered trademark of Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. Bosulif is a registered trademark of Pfizer Inc.